Interested in this kind of news?
Receive them directly in your inbox. Delivered once a week.
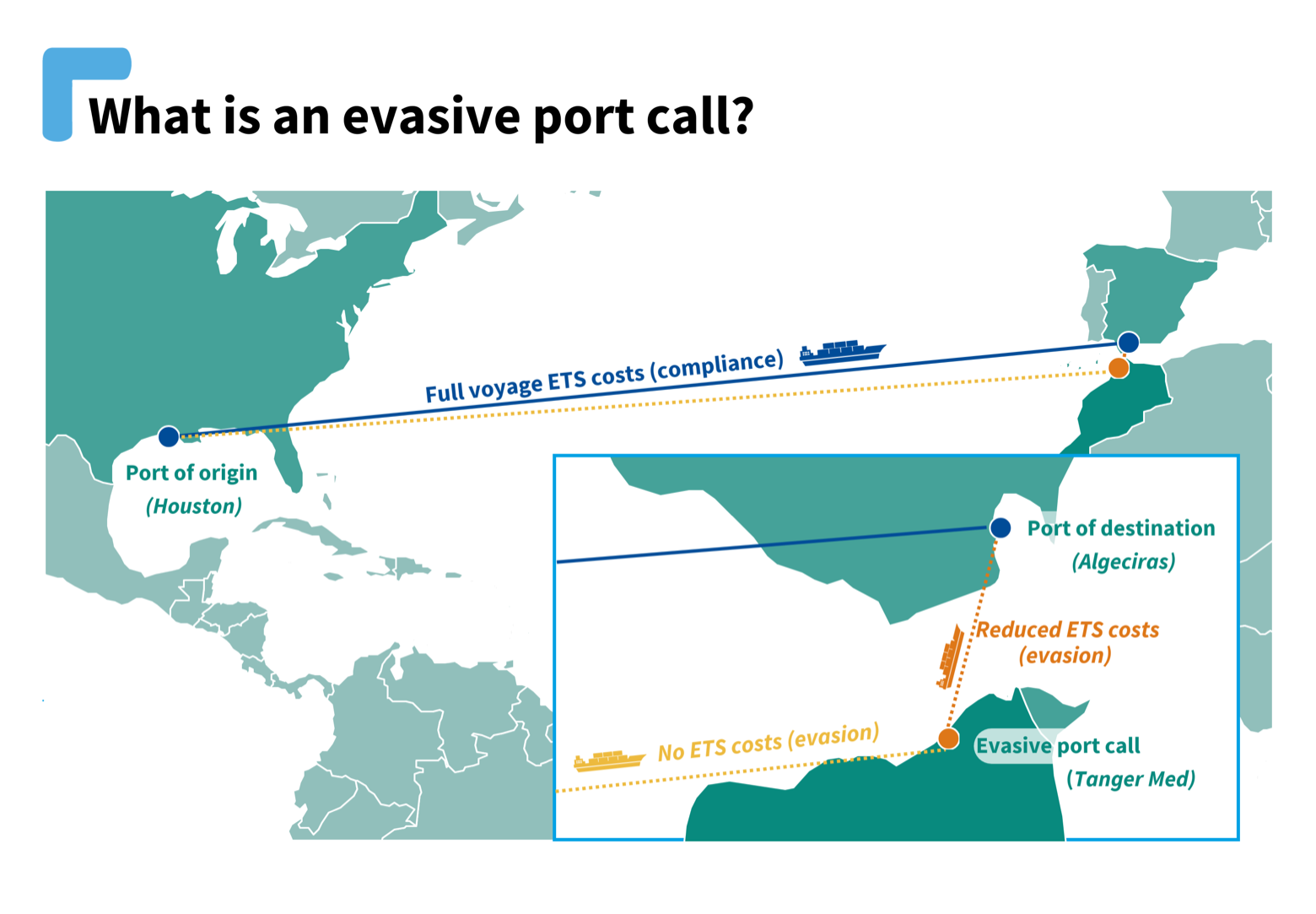
The findings come as EU regulators prepare a proposal to include shipping in the emissions trading system (ETS) and weigh up the benefits of covering all emissions (known as ‘full scope’) or simply trade within the EU.[1] A ship from Houston, for example, could stop at Morocco before it reaches Spain and then only buy pollution permits for the short, final leg of the voyage. Yet as T&E’s study of tens of thousands of port combinations shows, the savings from evading a full-scope ETS would be just 7%, due to extra costs including fuel and port charges. With an ETS covering half the long-distance voyage (‘semi-full scope’), the benefits of evasion are non-existent, the study finds.
Sofie Defour, shipping officer at T&E, said: “The study demonstrates that horror stories of massive carbon leakage if ships were included in a carbon market are false. The EU has little to fear from shipowners evading its ports to make non-existent savings. It’s high time it made the sector start paying for its pollution.”
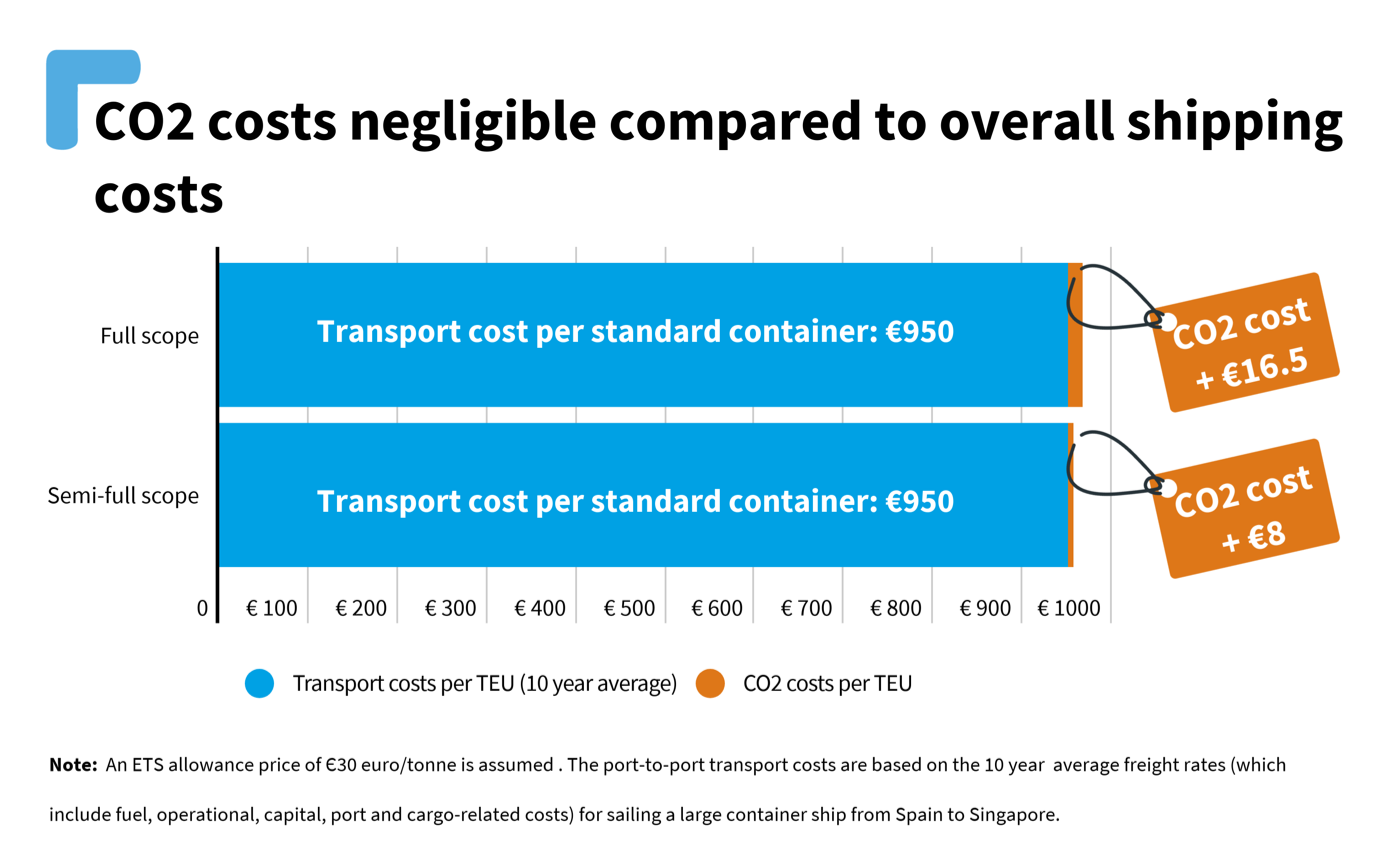
Ship-owners would face minimal costs in a ‘full-scope’ ETS covering all emissions on voyages to and from the EU. Pollution permits for transporting a standard container from Spain to Singapore would be less than 2% of the overall transport cost, dropping to less than 1% if the ‘semi-full scope’ would be included. T&E said the EU should defy industry scaremongers and cover long-distance shipping emissions in its carbon market and not just pollution on voyages within Europe.
Sofie Defour said: “Limiting the EU’s carbon market to maritime emissions between European ports lets shipping off the hook for a large share of its pollution. It would also forfeit ETS revenues that could be reinvested in greening the sector.”
In 2019, the European Commission committed in its European Green Deal to extend the ETS to the maritime sector while the European Parliament has proposed to introduce a maritime ETS by 1 January 2022 as part of its revision of the EU MRV regulation.
ENDS
Note to editors:
[1] Intra-EU emissions make up only 40% of the EU shipping emissions, while the remaining 60% are due to long-distance shipping calling at EU ports. Both intra-EU and long-distance shipping are already covered by the monitoring and reporting obligations under the EU MRV Regulation.