As the negotiations on the ETS aviation unfold, long-haul flight emissions are likely yet again to be excluded from the scope of the Directive. Departing flights (extra-EEA flights) represent the biggest chunk of European aviation’s climate impact. Long-haul flights (those over 4000 km) represent approximately 6% of departing flights from the EEA but half of all CO2 and NOx emissions.
A majority of Member States in the Council are firmly standing on their position to continue to limit the scope of the ETS to intra-EEA flights only, claiming that CORSIA is the right instrument to cover international aviation. The recent renegotiation of CORSIA’s baseline at 85% of 2019 emissions levels, is brandished as a step in the right direction towards more climate ambition. In reality, CORSIA is a failure and ICAO is ineffective at regulating aviation emissions.
Transport & Environment and Carbon Market Watch are convinced that the scope of the ETS should be extended to all flights departing from an airport located in the EEA, as expressed in the European Parliament’s position. This would:
- Price more emissions: Today, the ETS excludes 58% of Europe’s aviation departing emissions. Including all departing flights would finally price long-haul flights according to their impact on the climate.
- Raise revenues: It would also mean an increased source of revenues to finance the green transition in the industry and beyond. Under the current EU ETS proposal, revenues generated by the purchase of allowances by airlines between 2024 and 2030 would amount to €39 billion. Auctioning revenues for a scope including all EEA departing flights would amount to €97 billion for a similar period if we follow the European Parliament’s proposal.
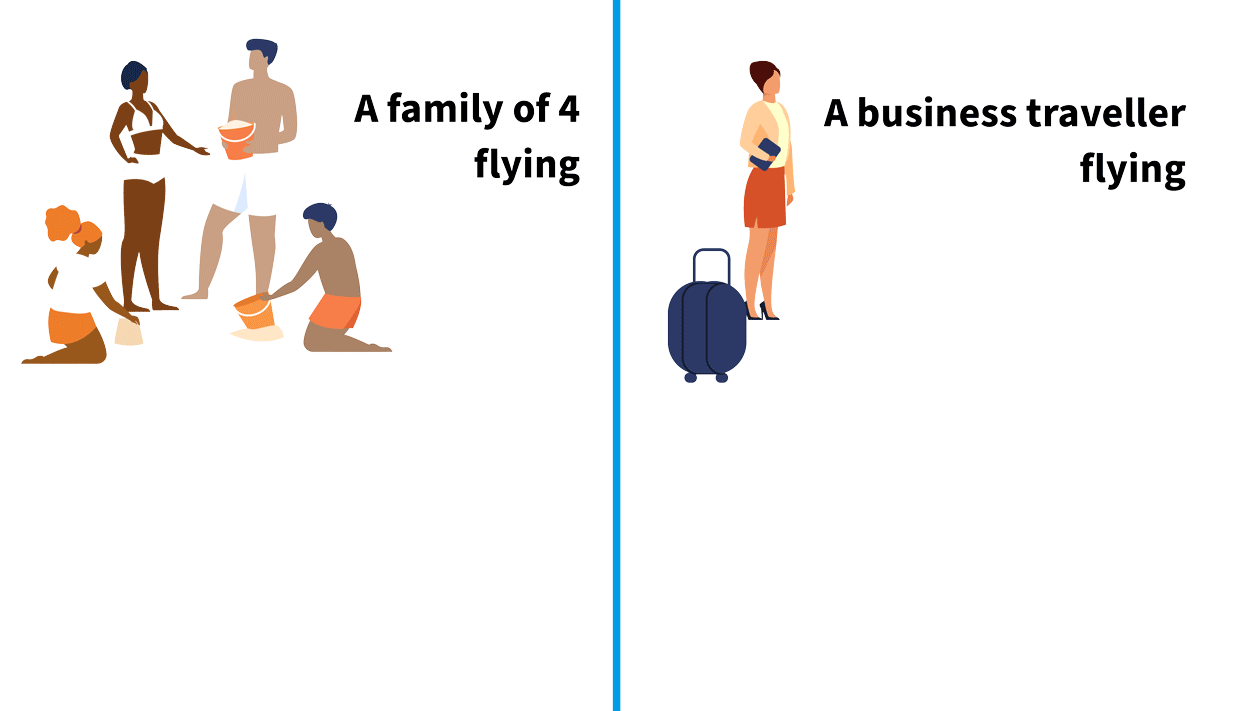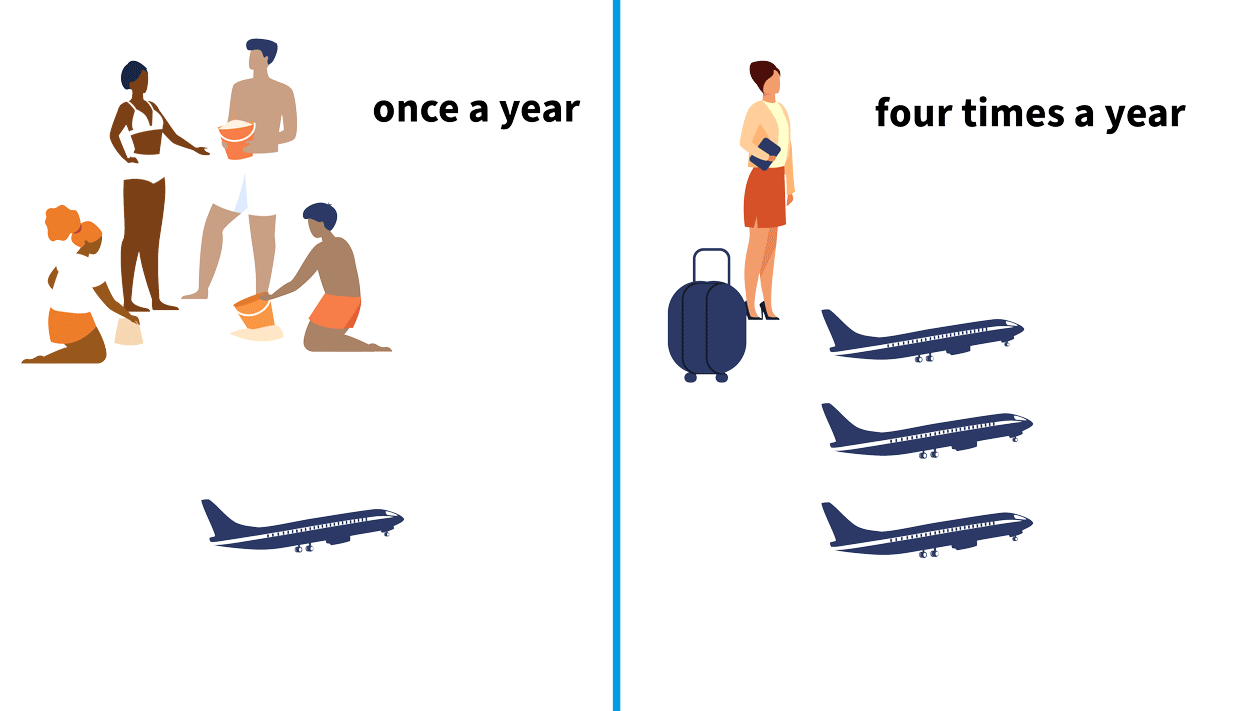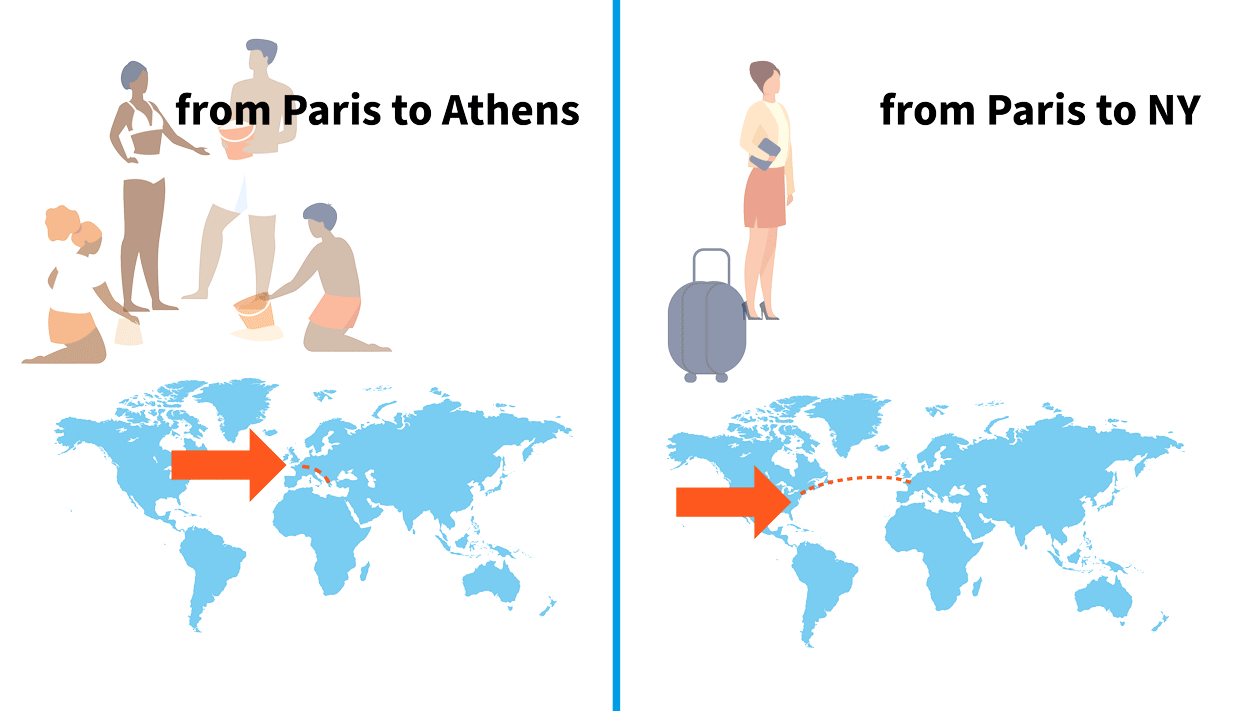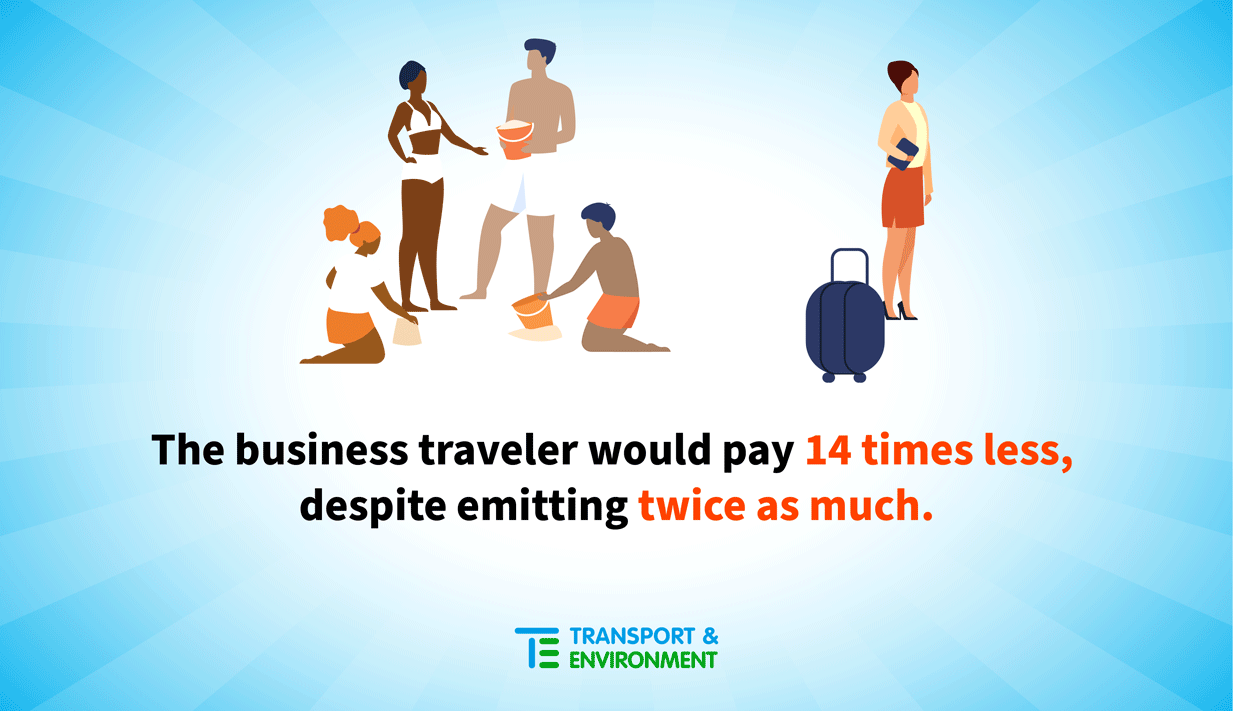
- Repair a social injustice: Continuing to exclude international aviation from climate measures using the excuse that aviation is an “international mode of transport” is no longer acceptable, it is unfair to citizens, and sends the wrong signal. For instance today, a family of 4 flying economy for its annual holiday from Paris to Athens emits 1688 kg of CO2 and pays a total of €169 under the ETS. By contrast, a business traveler flying 4 times from Paris to New York emits 3344 kg of CO2 and only pays €12 under CORSIA.